|
Strength of materials online |
 |
Site menuBeam calculation (analysis) for strength online - curves Mx, Qy, Mtor, N, finding the maximal bending moment Mx, maximal moving force Qy. Statically indeterminable beams can be calculated too!!. All is easy! For Free! FEA online. Truss, frame, beam analysis (calculation) for strength online - reactions, curves M, Q, M, N. Software (downloads) - useful programs (diagrams, calculators, etc). Forum - find answers or ask a question. |
Tensile Strength TestStretching Wires
Tensile Strength Test for Various Metals
Objective:
The objective of this experiment is to demonstrate the elastic and plastic properties of metals.
Time: 50 minutes
Review of Scientific Principles:
Wires of the same gauge, but made of different metals typically support different loads (masses) before going through the point at which they change from being elastic to being plastic. Elastic deformation is recoverable after the load is removed. Plastic deformation is not recoverable.
Applications:
In order to use metals in particular applications, it is sometimes necessary to know their tensile strength. To avoid failure, the right metal must be used.
Materials and Supplies:
15 to 20 cm long pieces of 16 or 18 gauge wire of copper, aluminum, steel, etc. wires saved from experiment 3 ring stand adjustable single-burette clamp meter stick small paper cup (a 1-oz) paper cup works well) variable masses (lead shot or small ring-washers)
Procedure:
Diagram of Set-up:
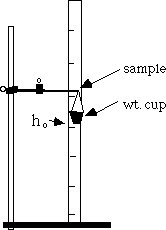
Data:
Analysis:
1. From your data collected in Part III, generate a data table for each wire; including the values for mass, height, and displacement (height - ho).
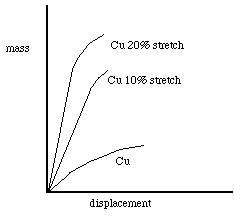
2. Plot a graph of mass (on vertical axis) versus displacement for each of the different types of wires. Note that the slope of the curve represents the relative stiffness of the wire represented by the curve. See sample graph.
3. For each of the types of metal wires, find the maximum mass for which the curve remained basically a straight line (the slope was constant). This defines the yield strengths of the metal.
Questions:
1. What is happening to the bonded metal atoms during elastic deformation?
2. What is happening to the bonded metal atoms during plastic deformation?
3. Give the maximum mass placed on each wire before permanent deformation occurred.
4. Why would an engineer be interested in the yield strength of a metal for a particular application?
Teacher Notes:
Answers to Questions:
1. The bonds between the atoms are stretching.
2. Metal atoms are sliding past each other.
3. Student answers.
4. In most applications, it is not desirable to exceed the yield strength of the product. If the yield strength is exceeded the object will be permanently deformed and likely will no longer be useful. |
EntryRecommended |
|
Using the contents of this site, a resource link is required.
© Dmitry Terekhov, 2004-2020. |